

Embarking on the journey of buying a business is one of the most significant financial decisions you’ll ever make. Without a structured approach, it’s easy to overlook critical details that could turn a promising opportunity into a costly mistake. The excitement of ownership can often overshadow the meticulous work required to vet a company properly. This is where a detailed buying a business checklist becomes your most valuable asset. It transforms the complex, often chaotic process into a manageable, step-by-step framework, ensuring you examine every facet of the business, from its financial health and legal standing to its operational efficiency and market position.
This guide provides an exhaustive 8-step checklist designed to empower you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the acquisition process. We will move beyond surface-level advice to provide actionable insights and practical steps for each stage of your evaluation. Think of this as your strategic roadmap, helping you ask the right questions, identify potential red flags, and accurately assess the true value of any potential acquisition.
From deep-diving into financial records and scrutinizing legal documents to evaluating customer concentration and planning a seamless transition, each point on this checklist is a crucial milestone. Following this comprehensive guide will help you mitigate risk, negotiate from a position of strength, and ultimately secure a deal that sets you and your new venture up for long-term success. Let’s begin the process of making a smarter, more informed acquisition.
The cornerstone of any sound business acquisition is a meticulous financial investigation. This is far more than just a cursory glance at the seller’s profit and loss statements; it is a deep, forensic examination of the company’s financial history and health. This critical step on your buying a business checklist involves verifying the seller’s financial claims, identifying potential liabilities, and understanding the true, sustainable profitability of the enterprise. You must scrutinize at least three to five years of detailed financial records to build an accurate picture.

Financial due diligence directly impacts the business valuation and your offer price. It uncovers the story behind the numbers, revealing trends, risks, and opportunities that are not immediately obvious. Ignoring this step is like buying a house without an inspection; you might inherit costly, hidden problems that could jeopardize your investment.
Key Insight: The goal isn’t just to verify past performance but to confidently project future cash flow. Your analysis should determine the business’s ability to service debt, fund operations, and provide a return on your investment.
To execute this step effectively, follow a structured process:
Just as vital as the financials, a rigorous legal due diligence process protects you from inheriting unforeseen liabilities and ensures the business is operating on solid legal ground. This step on your buying a business checklist involves a comprehensive examination of all corporate documents, contracts, licenses, intellectual property, and regulatory compliance. It verifies that you are acquiring clear title to all assets and that the business you are buying is not a legal minefield waiting to explode.
Legal due diligence confirms the legitimacy of the business and its assets. It can uncover deal-breaking issues, such as ownership disputes, pending lawsuits, or critical permits that cannot be transferred. Skipping this step is a high-stakes gamble that could result in you purchasing a business you cannot legally operate or one burdened with crippling financial and legal obligations from its past.
Key Insight: A clean legal history is just as important as a profitable one. This review ensures the business’s legal foundation is sound, protecting your investment from costly litigation and compliance failures down the road.
To properly navigate the legal complexities, you must be methodical:
Beyond the balance sheet, the lifeblood of any business is its customers. A thorough customer and revenue analysis is a non-negotiable part of your buying a business checklist, moving your investigation from historical financials to future viability. This step involves a deep dive into the company’s customer base to understand revenue stability, concentration risks, and the sustainability of its income streams. You are not just buying assets and cash flow; you are buying customer relationships and a market position.

This analysis directly validates the quality and predictability of the company’s revenue. A business with a diversified, loyal customer base is inherently less risky and more valuable than one dependent on a few key accounts. Uncovering the dynamics of customer relationships helps you assess potential threats, such as contract expirations or declining satisfaction, which could drastically impact post-acquisition performance.
Key Insight: The story of a business’s health isn’t just in its profits, but in who is generating those profits. Understanding customer loyalty, acquisition costs, and retention rates is essential for forecasting future revenue with any degree of confidence.
To conduct a meaningful customer and revenue analysis, be systematic:
A business’s financial health is critical, but its operational integrity is what determines its long-term viability and scalability. This step in your buying a business checklist involves a comprehensive evaluation of how the company functions day-to-day. You will dissect its workflows, technology infrastructure, supply chains, and overall efficiency to see if the engine runs smoothly or is held together by the current owner’s constant intervention. This assessment determines whether operations are sustainable and documented or dangerously dependent on a single person.

Strong, documented systems are the backbone of a valuable business. They ensure consistency, reduce errors, and make the company less reliant on any one individual. Discovering that a business lacks formal processes or runs on outdated technology late in the game can lead to significant, unforeseen capital expenditures and operational chaos post-acquisition. This step protects you from buying a job, not a self-sustaining enterprise.
Key Insight: A business without documented systems isn’t a business; it’s a practice highly dependent on its practitioner. Your goal is to acquire an asset that can operate and grow efficiently without its founder.
To properly evaluate the company’s operational foundation, follow this structured approach:
A business is often only as strong as its people. This part of your buying a business checklist moves beyond the numbers to assess the human capital, which can be the company’s most valuable, or riskiest, asset. It involves a thorough evaluation of the workforce, from key management to frontline staff, including organizational structure, compensation, morale, and any potential employment-related liabilities. Understanding this dynamic is critical for a smooth transition and long-term success.
The employees carry the operational knowledge, customer relationships, and cultural fabric of the business. An unstable or non-compliant workforce can create significant operational disruptions and legal expenses immediately after you take over. This review helps you understand who is critical to the business’s continuity, what it costs to retain them, and whether there are any hidden HR-related financial bombs waiting to detonate.
Key Insight: Your goal is to ensure the talent and knowledge required to run the business will remain after the owner exits. A great business with a disengaged or departing team is a failing business in disguise.
To properly evaluate the human resources component, take these steps:
A business does not operate in a vacuum. A thorough evaluation of its position within the broader industry and local market is a non-negotiable part of any buying a business checklist. This step involves an objective assessment of the company’s competitive advantages, market share, industry trends, and potential threats. Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for determining if the business has a sustainable future or if it’s operating on borrowed time.
This analysis determines the business’s long-term viability and growth potential. A company may have stellar financials today, but if the market is shrinking, or a disruptive competitor is on the horizon, its future value could plummet. This step protects you from overpaying for a business whose success is built on a shaky or eroding foundation.
Key Insight: The goal is to identify a business with a durable competitive advantage or “moat.” This could be a strong brand, unique intellectual property, exclusive supplier relationships, or a prime location that competitors cannot easily replicate.
To conduct a robust market analysis, go beyond the seller’s claims:
Arriving at the right price and structuring the deal correctly are where the art and science of buying a business truly converge. This step involves a comprehensive assessment to determine the fair market value of the business and then crafting optimal terms that protect your investment. This is not just about the final purchase price; it includes how that price is paid, the timeline for payments, and the tax implications for both you and the seller. Applying multiple valuation methodologies and negotiating a balanced deal structure are essential for ensuring the acquisition makes long-term financial sense.
A proper valuation ensures you don’t overpay, while a well-designed deal structure can mitigate risk and improve cash flow. An incorrect valuation can doom the deal from the start, burdening you with excessive debt. Similarly, a poorly structured deal can create unforeseen tax liabilities or fail to align the seller’s interests with a smooth transition. This is a pivotal part of the buying a business checklist where financial analysis meets strategic negotiation.
Key Insight: The best deal structures align incentives. Using tools like seller financing and earnouts ensures the seller remains invested in the business’s success post-closing, which is invaluable during the transition period.
This infographic illustrates a common deal structure timeline, breaking down how the purchase price can be paid out over several years.
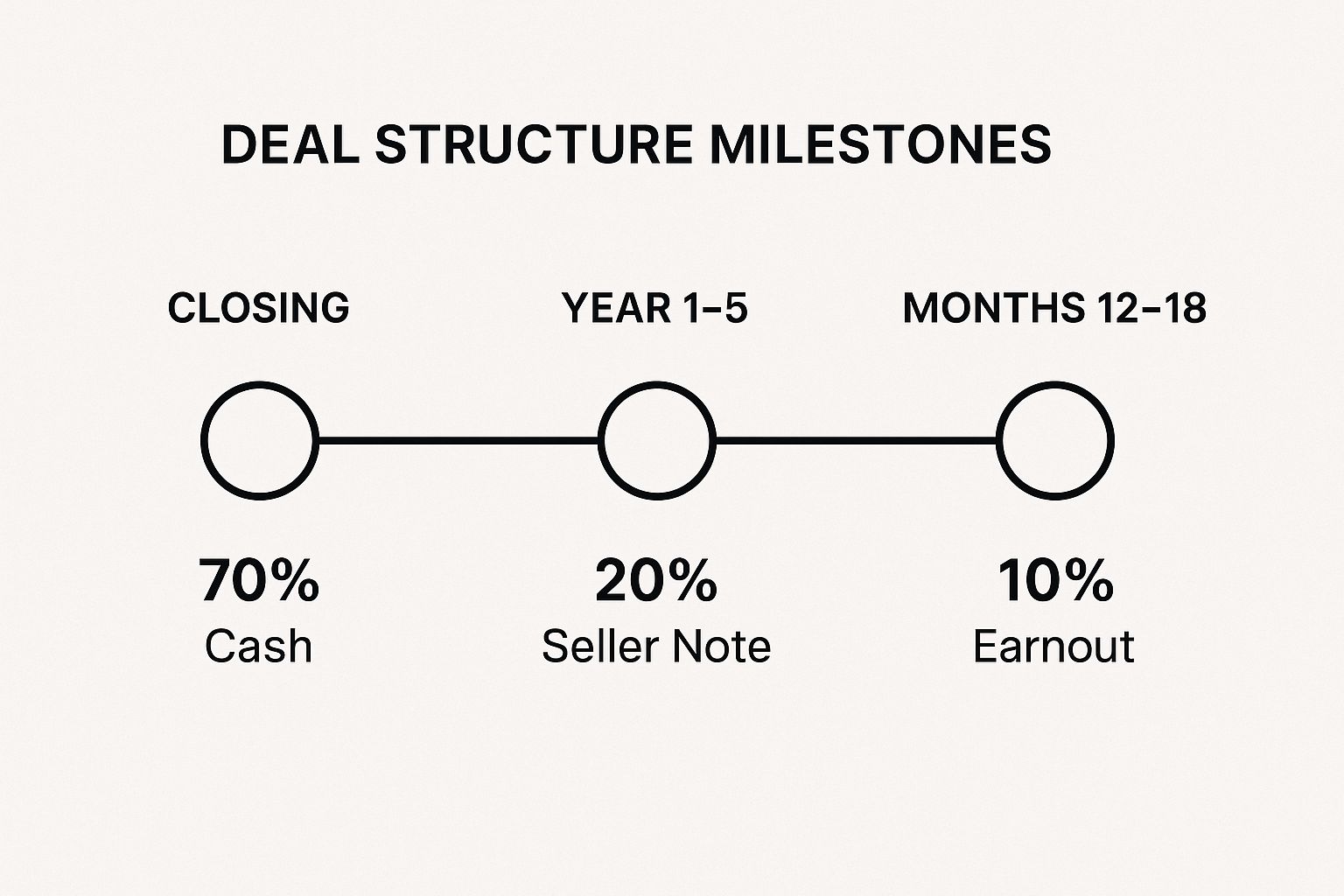
The visualization shows that the bulk of the payment happens upfront, while subsequent payments are tied to the business’s ongoing performance and the seller’s commitment.
To master this complex stage, focus on both the numbers and the negotiation strategy:
The deal is signed, but the most delicate phase is just beginning. A strategic transition and integration plan is the blueprint for preserving the value you just fought to acquire. This step on your buying a business checklist involves mapping out the transfer of ownership, knowledge, and relationships from the seller to you. It covers everything from the seller’s training period and employee retention to customer communications, ensuring business continuity and a smooth handover.

A poorly executed transition can quickly erode customer trust, alienate key employees, and disrupt critical supplier relationships, destroying a significant portion of the business’s goodwill overnight. A well-documented plan prevents operational chaos and sets the stage for future growth by ensuring that essential knowledge and processes are not lost when the previous owner exits.
Key Insight: The success of an acquisition is often determined in the first 90 days. A proactive, well-communicated transition plan minimizes uncertainty and builds confidence among employees, customers, and suppliers, protecting your investment from day one.
To build and execute a successful transition plan:
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Due Diligence and Records Review | High: requires specialized accountants | High: expert CPA/audit resources needed | Accurate valuation, detection of financial risks | Businesses with complex financial histories | Reveals true financial health, uncovers liabilities |
| Legal Structure and Documentation Review | High: needs experienced legal counsel | High: legal fees and deep contract review | Clear asset ownership, legal risk mitigation | Businesses with complex legal and regulatory issues | Prevents legal liabilities, protects IP rights |
| Customer and Revenue Analysis | Medium: data collection and analysis | Medium: access to customer data and systems | Revenue stability insight, customer risk analysis | Revenue-dependent or subscription-based firms | Identifies revenue risks, forecasts growth |
| Operations and Systems Assessment | High: requires operational expertise | Medium-High: process reviews, site visits | Operational scalability and risk identification | Manufacturing, retail, tech businesses | Identifies efficiency improvements, transition costs |
| Employee and Human Resources Evaluation | Medium-High: HR expertise needed | Medium: employee data and interviews | Workforce stability, key employee retention | Labor-intensive or key personnel-dependent businesses | Highlights key employees, reveals HR risks |
| Market Position and Competitive Analysis | Medium: research & industry expertise | Medium: market and competitor data access | Competitive advantage and market sustainability | Businesses in competitive or changing industries | Validates growth potential, identifies threats |
| Valuation and Deal Structure Analysis | High: complex financial modeling | High: valuation experts, legal & tax advice | Optimized purchase price and deal terms | All acquisitions requiring fair market price | Minimizes overpayment, structures risk |
| Transition and Integration Planning | Medium-High: detailed planning needed | Medium: time from seller and buyer | Smooth ownership change, business continuity | Businesses with operational complexity and key people | Maintains operations, ensures knowledge transfer |
Acquiring a business is one of the most significant professional endeavors you can undertake. It’s a journey filled with immense opportunity but also punctuated by critical decision points and potential pitfalls. This comprehensive “buying a business checklist” serves as your strategic roadmap, guiding you through the intricate layers of due diligence, valuation, and integration. It transforms an overwhelming process into a series of manageable, actionable steps.
Moving from initial interest to a closed deal requires more than just a checklist; it demands a disciplined, analytical, and forward-thinking mindset. Each item we’ve explored, from scrutinizing financial records to planning for a seamless transition, represents a crucial piece of the acquisition puzzle. Ignoring even one area, such as a deep dive into customer concentration or a thorough assessment of employee morale, can expose your investment to unforeseen risks long after the papers are signed.
As you move through this process, your primary goal is to build a complete, unvarnished picture of the target business. This isn’t about finding a “perfect” company, as none exist. Instead, it’s about understanding the reality of the opportunity: its strengths, its weaknesses, its untapped potential, and its inherent challenges.
Think of your due diligence findings as building blocks for your final decision and negotiation strategy:
Key Insight: A successful acquisition is not defined by a flawless due diligence process, but by how effectively you use the information gathered to structure a fair deal, mitigate risks, and create a concrete plan for post-closing success.
Completing this checklist is a monumental task, but it marks the beginning of the next phase. Your immediate next steps should be to consolidate your findings into a cohesive analysis. Create a final due diligence report that summarizes your conclusions for each of the eight key areas. This document will be the foundation for your final negotiation with the seller.
Remember, the goal is not to “win” the negotiation but to arrive at a mutually beneficial agreement that reflects the true value and risk profile of the business. Be prepared to walk away if the terms don’t align with your financial models and risk tolerance. A disciplined approach, guided by the data you’ve meticulously gathered, is your greatest asset. By diligently following this “buying a business checklist,” you empower yourself to make an informed, confident, and ultimately profitable acquisition.
Navigating the complexities of a business acquisition, especially in a dynamic market like Las Vegas, requires expert guidance. The team at Vic & Wayne Brokers specializes in turning this checklist into a successful transaction, leveraging over 30 years of combined experience to manage due diligence, negotiations, and closing. If you are ready to take the next step with confidence, connect with Vic & Wayne Brokers to ensure your acquisition journey is smooth and successful.